Preface
Goal: Copy A Range of Cell Along with All Properties.
-
Using LibreOffice UNO Macro,
-
Using Faktur Pajak (Indonesian Tax) as Example,
-
This article is the first part of two articles.
Proper document handling is required, when your quiet messy company, suddenly audited by public accountant.
1: The Challenge
Tidying? Don’t you have better thing to do?
Have you ever on your job met a spreadsheet with a so many table header, sooo long, that you can’t even print without additional paper?
For example this sheet below:
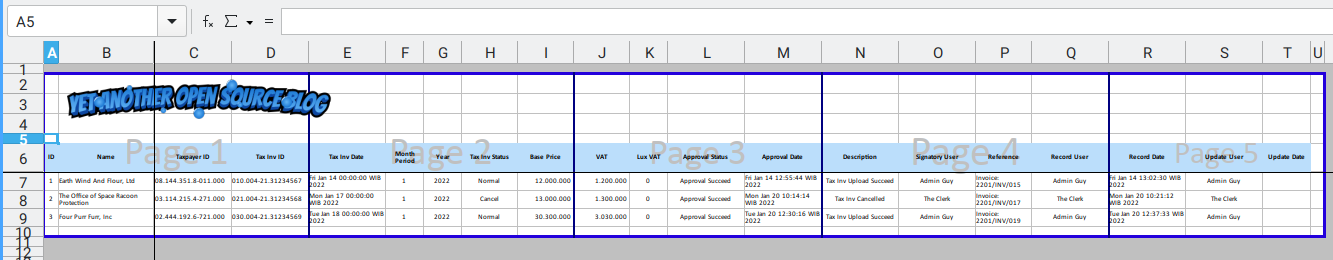
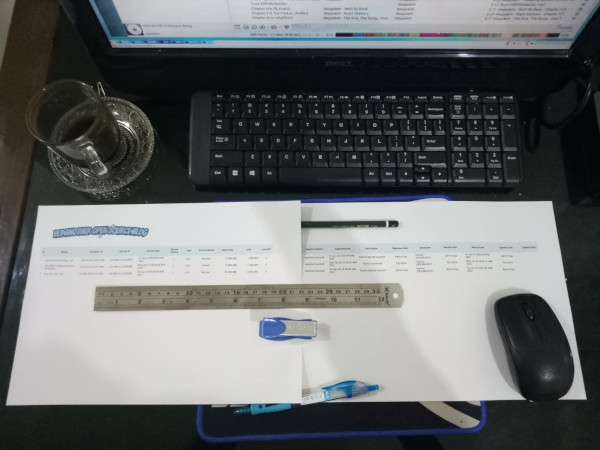
And when you print the table:

Actually you can translate the table looks, into form view as below, with just simple translation script.
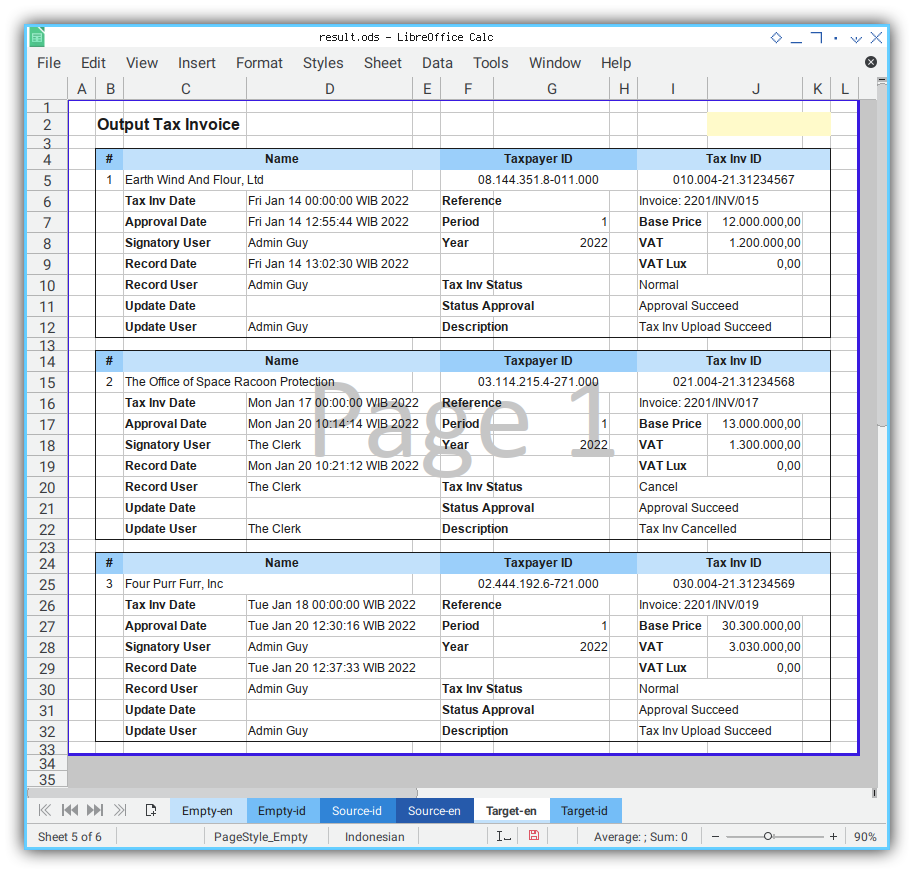
The real life printed result can be seen as below:
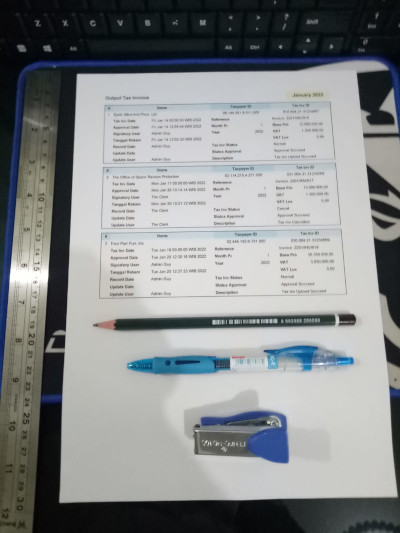
It is easy, when all you have is just those two row of data as above. But how about thousands of data? You can create yourself a script. Execute, and voila, those thousand rows is already exported, into the form.
cuman orang gabut yang sempet ngerapi-rapi-in
Designing Template
Our challenge is field translation. Before we ever need to translate, we need to create a template.
All I do is just put source table, and form view, side by side. And manually moved the field one by one.
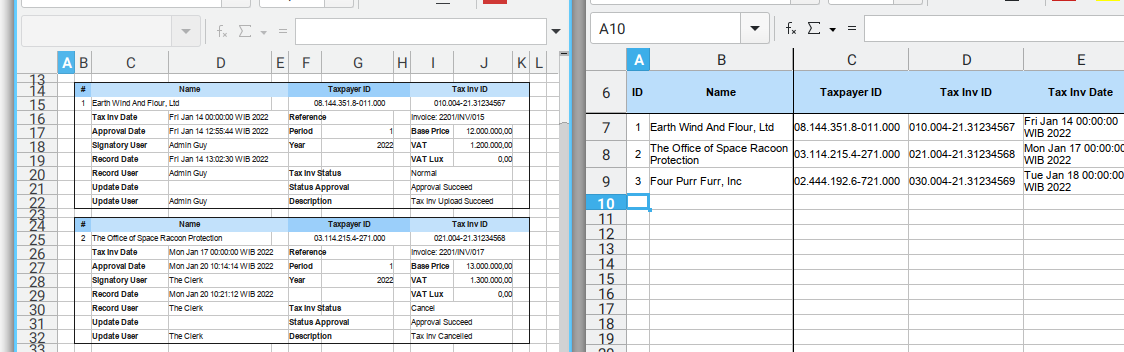
This task is not as easy as I was thinking. I need to create a few design, and designing form, also takes time.
Provided Example Data
I have provided example sheets, with complete form, along with each properties. Such as different number format and so on.
You can download the artefact for simple range copying here below. Each sheet, I provide two languages. You should choose only one over another.
- Source: [source.ods]
After macro execution you can get the example result here
- Target: [target.ods]
Based on that mockup design above we can make a template.
- Template: [template.ods]
Then we can continue combine with sheet with long columns, along with dummy data.
- Data: [data.ods]
With these template and data, wen can finally get our final result, the completely filled form.
- Result: [result.ods]
Copying Issue
Have you ever have a difficulties to copy cells range programatically?
Copying cells using libreoffice,
require copying of these two attributes:
- Basic Attribute
- Row Height
2: Using Python LibreOffice Macro
Testing
The scariest part is getting started. Once it run, I can continue with good mood.
I always have this fear when I start something new, so I push myself to start code as small as possible, then suddenly my fear vanished.
Minimal
LibreOffice Macro required this line below at the top.
# coding: utf-8
from __future__ import unicode_literalsNow consider, go straight to the code. Start from simple.
Skeleton
There is only consist one short file required. All definition shown here:
# coding: utf-8
from __future__ import unicode_literals
class CopyRange01:
def __init__(self, name):
def addressTest(self):
def run(self):
def main():Class Initialization
Just usual ritual, to summon holy worksheet.
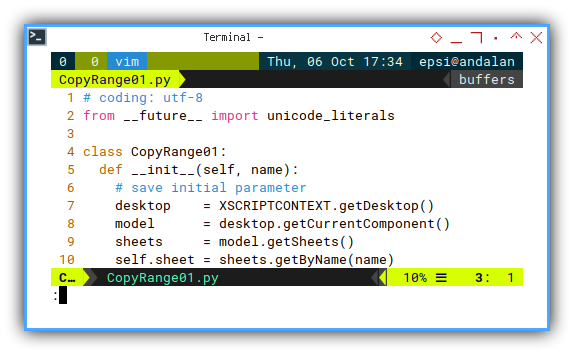
class CopyRange01:
def __init__(self, name):
# save initial parameter
desktop = XSCRIPTCONTEXT.getDesktop()
model = desktop.getCurrentComponent()
sheets = model.getSheets()
self.sheet = sheets.getByName(name)Debugging in Terminal
Just to remind myself, that I can always debug in APSO terminal. By printing any object properties.
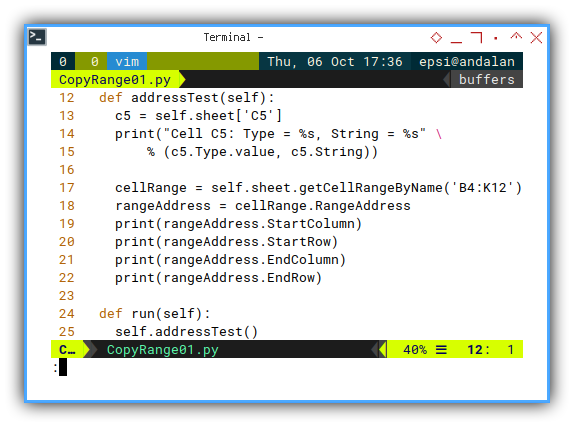
def addressTest(self):
c5 = self.sheet['C5']
print("Cell C5: Type = %s, String = %s" \
% (c5.Type.value, c5.String))
cellRange = self.sheet.getCellRangeByName('B4:K12')
rangeAddress = cellRange.RangeAddress
print(rangeAddress.StartColumn)
print(rangeAddress.StartRow)
print(rangeAddress.EndColumn)
print(rangeAddress.EndRow)I avoid harcoded parameter,
but for starting point,
I can test the range properties for range B4:K12.
We will mve them to main section later.
Run: Execute
This is still very simple at the beginning.
def run(self):
self.addressTest()Main: Program Entry Point
All parameter defined here:
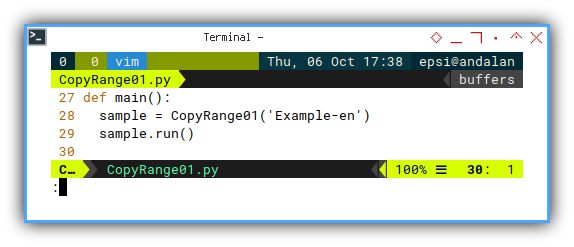
def main():
sample = CopyRange01('Example-en')
sample.run()This is just a very simple class initialization, so I can have skeleton to write more code.
APSO Menu
You can take a look what Macro we have written so far.
And open the PYthon Terminal.
Python Terminal with APSO
Just type main() and enter.
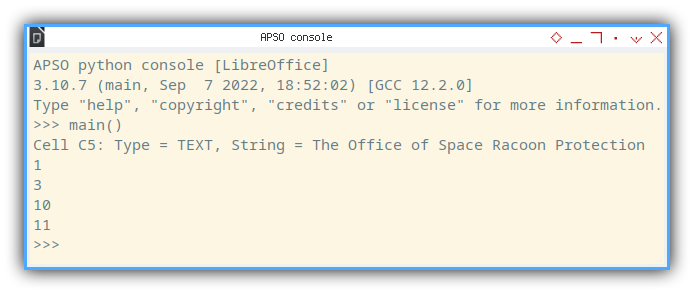
APSO python console [LibreOffice]
3.10.7 (main, Sep 7 2022, 18:52:02) [GCC 12.2.0]
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> main()
Cell C5: Type = TEXT, String = The Office of Space Racoon Protection
1
3
10
11
>>> There is nothing to be shown here. Just make sure, the APSO terminal print something.
3: Simple Range Copying
Copying Within The Sheet
Skeleton
class CopyRange02:
def __init__(self, name):
def copyRange(self, stringRange, stringAddress):
def setPrintArea(self, stringRange):
def setRangeHeights(self, stringRange, stringAddress):
def run(self):
def main():Class Initialization
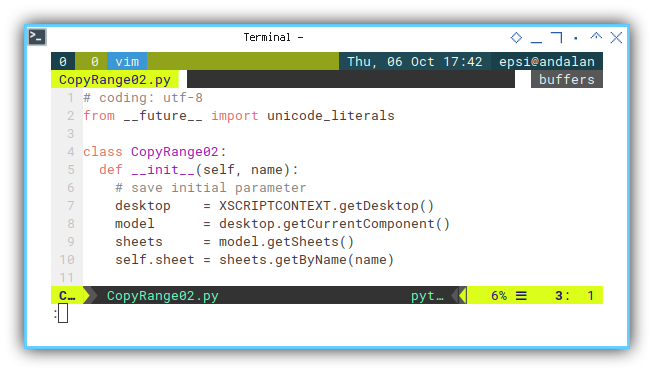
class CopyRange02:
def __init__(self, name):
# save initial parameter
desktop = XSCRIPTCONTEXT.getDesktop()
model = desktop.getCurrentComponent()
sheets = model.getSheets()
self.sheet = sheets.getByName(name)Main: Program Entry Point
Our testing parameter is still in run method inside the class.
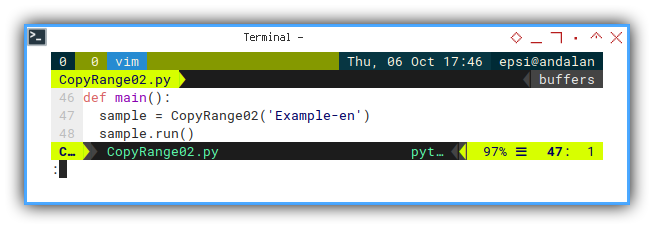
def main():
sample = CopyRange02('Example-en')
sample.run()We will fix this later.
Copy Range
Just use the API:
copyRangemethod.
It is a little bit tricky, even after googling stackoverflow. So I write this proper example to make it easier for us.
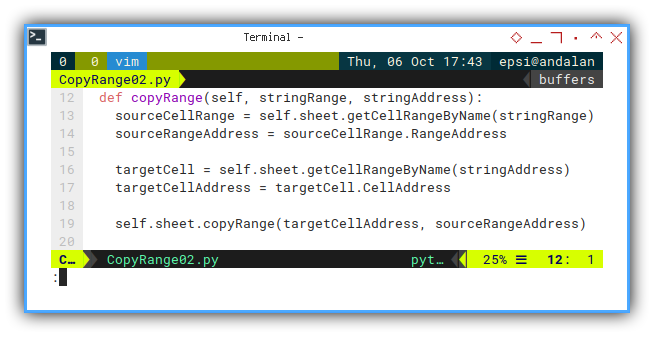
def copyRange(self, stringRange, stringAddress):
sourceCellRange = self.sheet.getCellRangeByName(stringRange)
sourceRangeAddress = sourceCellRange.RangeAddress
targetCell = self.sheet.getCellRangeByName(stringAddress)
targetCellAddress = targetCell.CellAddress
self.sheet.copyRange(targetCellAddress, sourceRangeAddress)And Run
def run(self):
self.copyRange('B4:K13', 'B14')Sheet Result
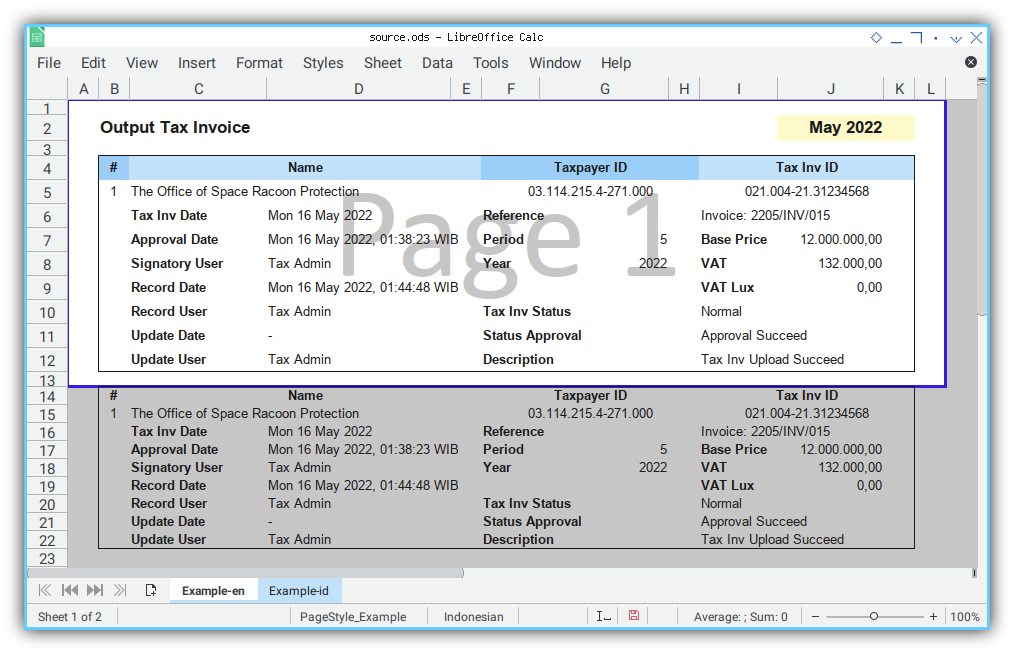
Looks cool right, but we need to better print area.
Setting Print Area
It is always tricky when it come to UNO. Even after reading the documentation properly. What we need is example code.
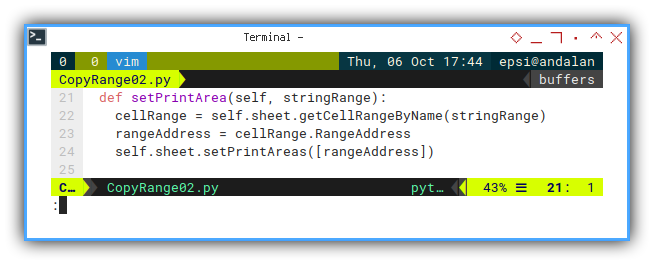
def setPrintArea(self, stringRange):
cellRange = self.sheet.getCellRangeByName(stringRange)
rangeAddress = cellRange.RangeAddress
self.sheet.setPrintAreas([rangeAddress])And Run
def run(self):
self.copyRange('B4:K13', 'B14')
self.setPrintArea('A1:L23')Sheet Result
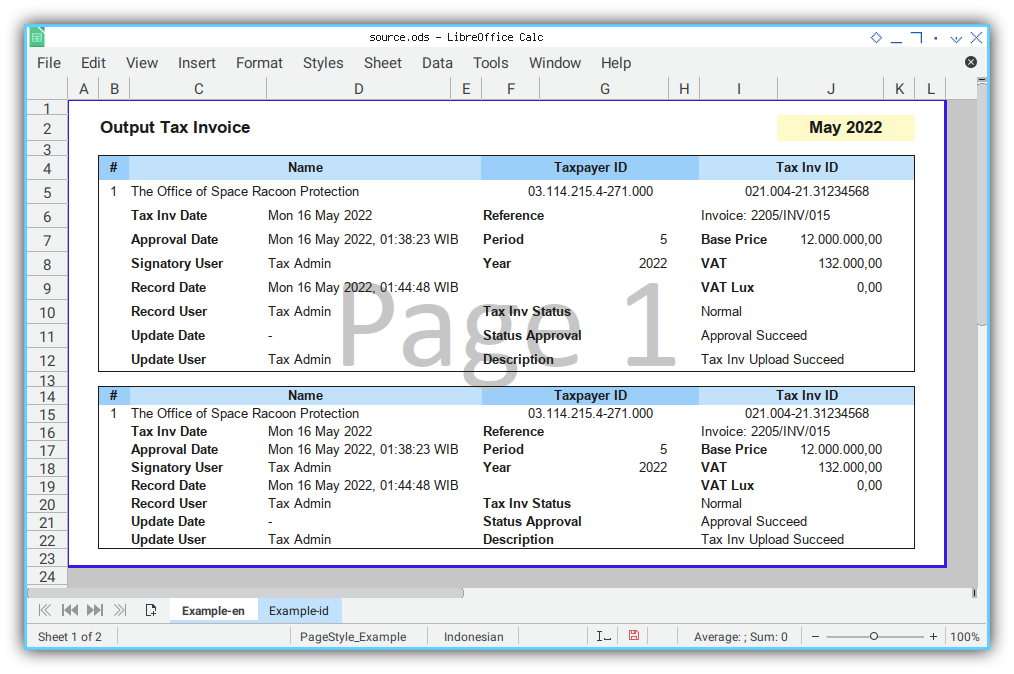
Can you spot something missing here? Why is it looks compressed
Yaps, the row height haven’t set properly.
Setting Row’s Height in Range
Calculating Offset
Walking for each row, assigning the same height with the original template.
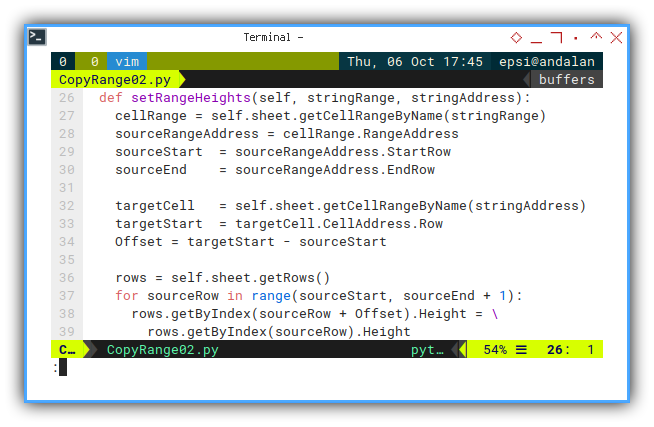
def setRangeHeights(self, stringRange, stringAddress):
cellRange = self.sheet.getCellRangeByName(stringRange)
sourceRangeAddress = cellRange.RangeAddress
sourceStart = sourceRangeAddress.StartRow
sourceEnd = sourceRangeAddress.EndRow
targetCell = self.sheet.getCellRangeByName(stringAddress)
targetStart = targetCell.CellAddress.Row
Offset = targetStart - sourceStart
rows = self.sheet.getRows()
for sourceRow in range(sourceStart, sourceEnd + 1):
rows.getByIndex(sourceRow + Offset).Height = \
rows.getByIndex(sourceRow).HeightAnd Run
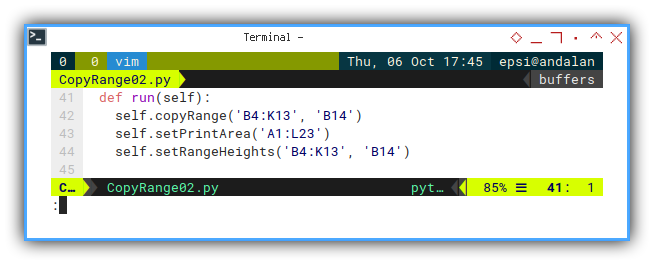
def run(self):
self.copyRange('B4:K13', 'B14')
self.setPrintArea('A1:L23')
self.setRangeHeights('B4:K13', 'B14')Sheet Result
The result are verbatim copy, as shown in figure below:
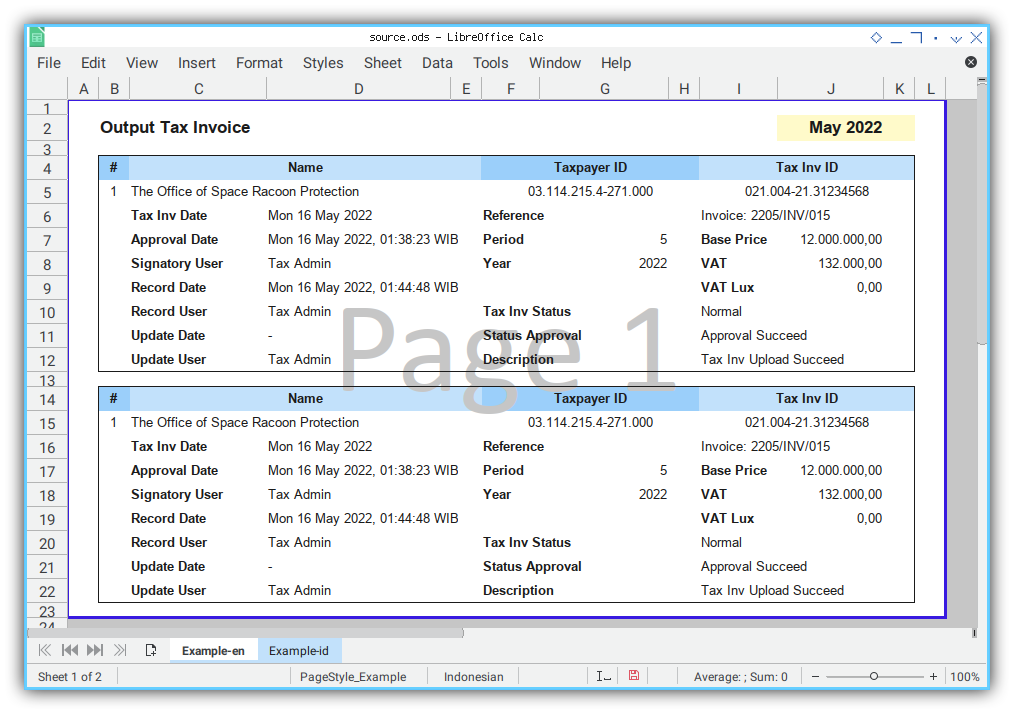
The next step, we need to prepare the class, so that the class can be utilized from other place.
4: Enhance Range Copying
Copying to Other Sheet: Source to Target
Skeleton
class CopyRange03:
def __init__(self, sName, tName):
def copySheet(self):
def calculateOffset(self, rangeAddr, index):
def copyRange(self, strRange, index):
def setRangeHeights(self, strRange, index):
def setPrintArea(self, strRange):
def run(self, stringRange, index):
def main():Class Initialization
We have two sheet names.
- Source sheet, and
- Target sheet

The initialization parameter should setup both sheet names.
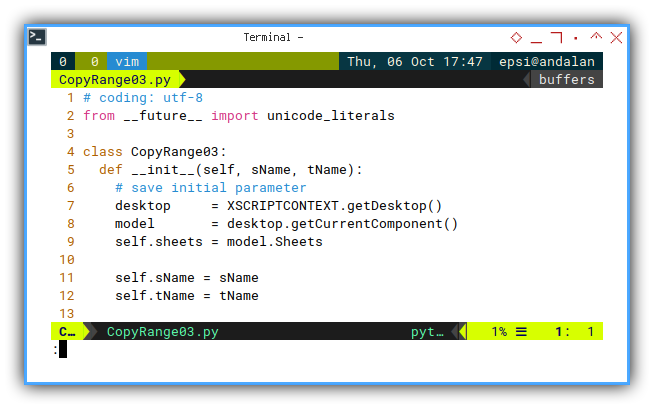
class CopyRange03:
def __init__(self, sName, tName):
# save initial parameter
desktop = XSCRIPTCONTEXT.getDesktop()
model = desktop.getCurrentComponent()
self.sheets = model.Sheets
self.sName = sName
self.tName = tNameRun: Execute
In order to make the class more flexible,
we manage the loop logic, outside the class.
So the run method only run for one index at a time.
This method also setup both sheet objects.
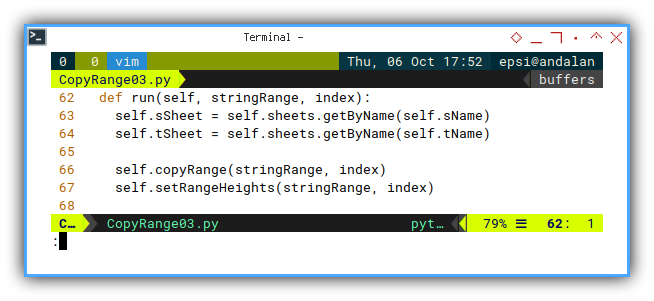
def run(self, stringRange, index):
self.sSheet = self.sheets.getByName(self.sName)
self.tSheet = self.sheets.getByName(self.tName)
self.copyRange(stringRange, index)
self.setRangeHeights(stringRange, index)Main: Program Entry Point
Here comes all the parameter argument, along with the loop logic.
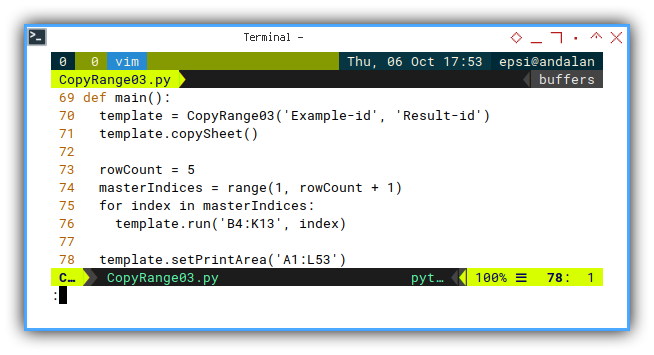
def main():
template = CopyRange03('Example-id', 'Result-id')
template.copySheet()
rowCount = 5
masterIndices = range(1, rowCount + 1)
for index in masterIndices:
template.run('B4:K13', index)
template.setPrintArea('A1:L53')Now, with so many method, where do we begin?
Copy Sheet
Short and Simple
This is somewhere inside the initial documentation.
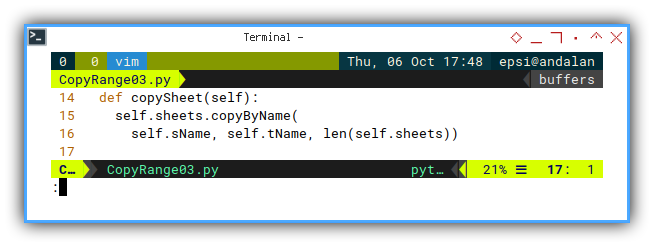
def copySheet(self):
self.sheets.copyByName(
self.sName, self.tName, len(self.sheets))Note that copySheet() call is not required in the next step,
because this would be handled by other class.
This is why I do not put this method within the run method.
Calculate Offset
The heart of cell address management.
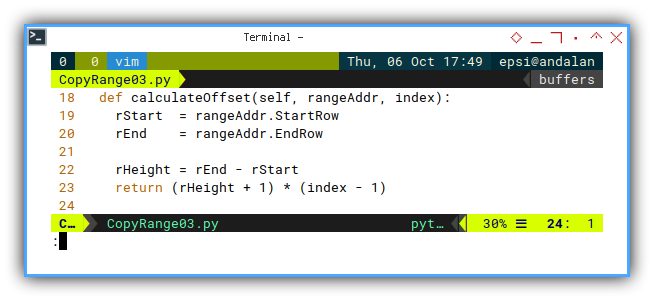
def calculateOffset(self, rangeAddr, index):
rStart = rangeAddr.StartRow
rEnd = rangeAddr.EndRow
rHeight = rEnd - rStart
return (rHeight + 1) * (index - 1)In this example, for every one index increment, we will have ten offset increment.
Copy Range
Just address translation
This is where we use the offset value.
Although this looks complex. This is actually just getting the right range/cell address, to be copied. And nothing more
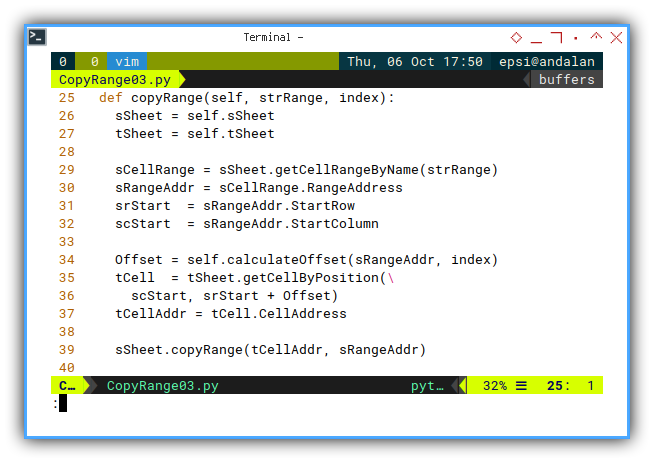
def copyRange(self, strRange, index):
sSheet = self.sSheet
tSheet = self.tSheet
sCellRange = sSheet.getCellRangeByName(strRange)
sRangeAddr = sCellRange.RangeAddress
srStart = sRangeAddr.StartRow
scStart = sRangeAddr.StartColumn
Offset = self.calculateOffset(sRangeAddr, index)
tCell = tSheet.getCellByPosition(\
scStart, srStart + Offset)
tCellAddr = tCell.CellAddress
sSheet.copyRange(tCellAddr, sRangeAddr)Setting Row’s Height in Range
Just another address translation
This is also where we use the offset value.
Just transform cell address. And that’s all.
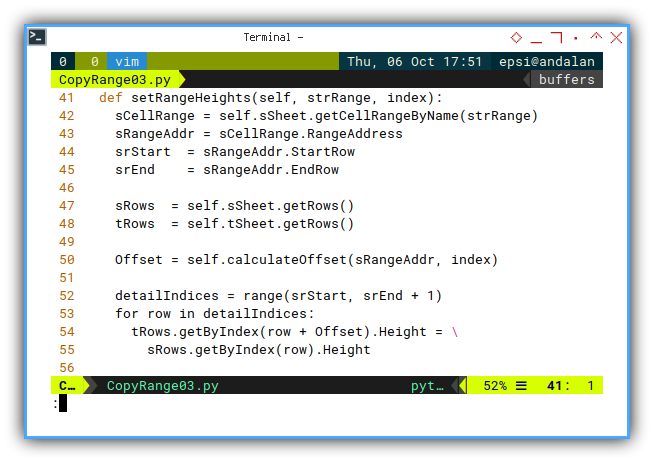
def setRangeHeights(self, strRange, index):
sCellRange = self.sSheet.getCellRangeByName(strRange)
sRangeAddr = sCellRange.RangeAddress
srStart = sRangeAddr.StartRow
srEnd = sRangeAddr.EndRow
sRows = self.sSheet.getRows()
tRows = self.tSheet.getRows()
Offset = self.calculateOffset(sRangeAddr, index)
detailIndices = range(srStart, srEnd + 1)
for row in detailIndices:
tRows.getByIndex(row + Offset).Height = \
sRows.getByIndex(row).HeightSetting Print Area
This is still simple
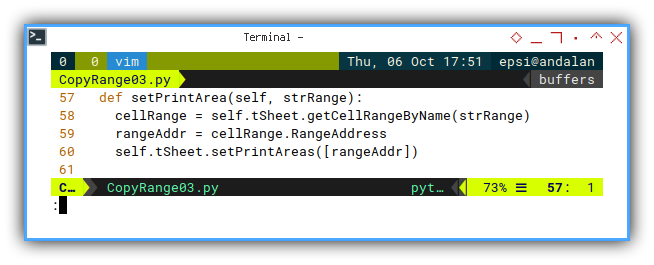
def setPrintArea(self, strRange):
cellRange = self.tSheet.getCellRangeByName(strRange)
rangeAddr = cellRange.RangeAddress
self.tSheet.setPrintAreas([rangeAddr])Result
With five row counts set in main().
def main():
...
rowCount = 5...The result will be:
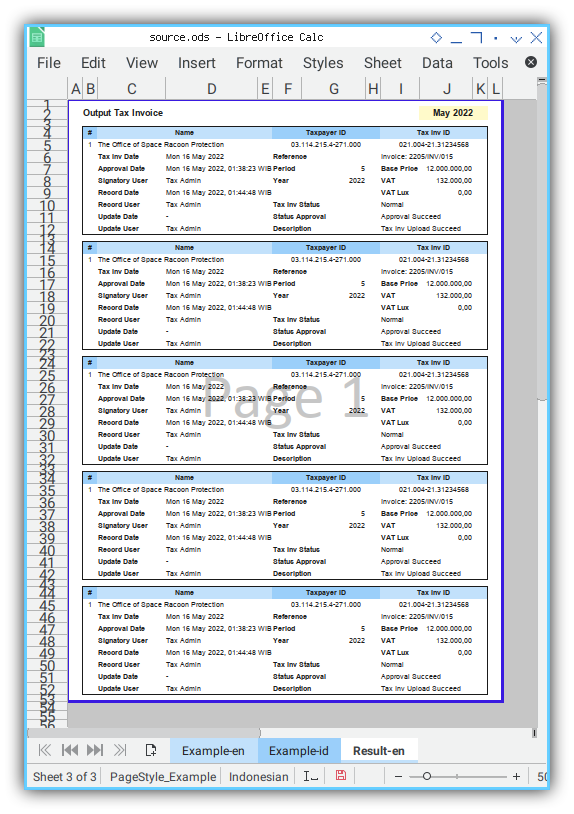
This is the final form for this class. But you don’t want all the page, to contain the same data over and over again right?
We are going to use entirely different class to handle the data. Inthe next article.
Using Other Language
You can set the language in main(),
for example Indonesia.
def main():
template = CopyRange03('Example-id', 'Result-id')or English
def main():
template = CopyRange03('Example-en', 'Result-en')The result will be reflected in sheet tab name.

We are done with class.
What is Next 🤔?
After copying range of cells, now is a good time to continue to fields translation.
Consider continue reading [ LibreOffice - Macro - Transform Field ].