Preface
Goal: Transform plain row based data into cute form view.
This article is the last part of two articles.
6: The Challenge
How to Automate?
Back to the Challenge This picture below is common in any business.
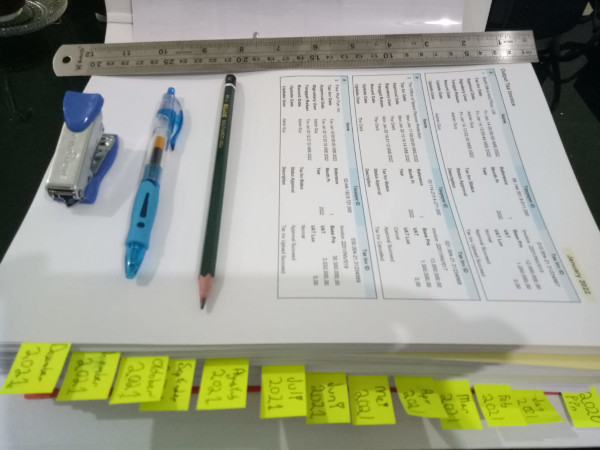
But how to speed up your workflow? Doing manually is extremely daunting task.
You need to spend your time to important task, rather than compiling data, right?
Of course you can do it with simpler script, so you can have the document compiled the worksheet, automatically for you.
All you need is just export the sheet to PDF. And you got the summary as below:
Prepare: English
Empty Template and Data Source
it is up to your choice whether you sue English or Indonesia. I provide both language.
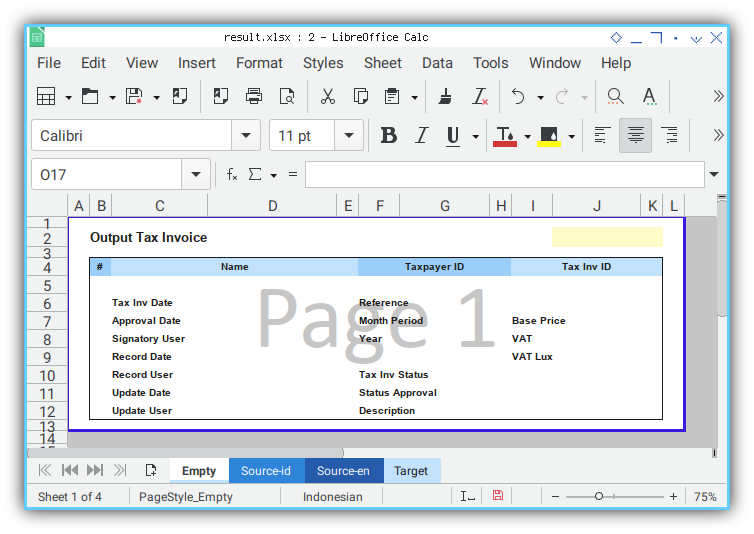
- Empty Template: template.xlsx
- Source Data: data.xlsx
After each exection of each python code,
you will get additional Target sheet:
- Result Sheet: result.xlsx
Prepare: Indonesia
Empty Template and Data Source
- Empty Template
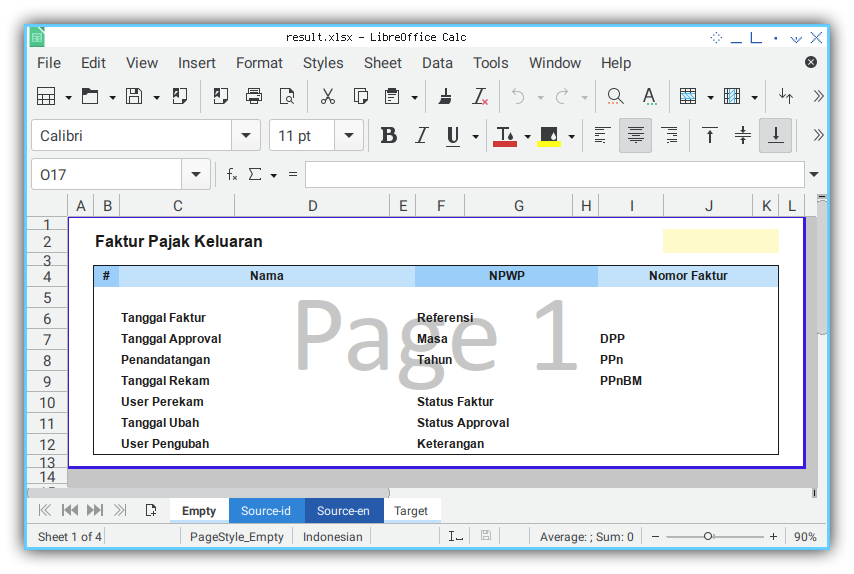
- Source Data
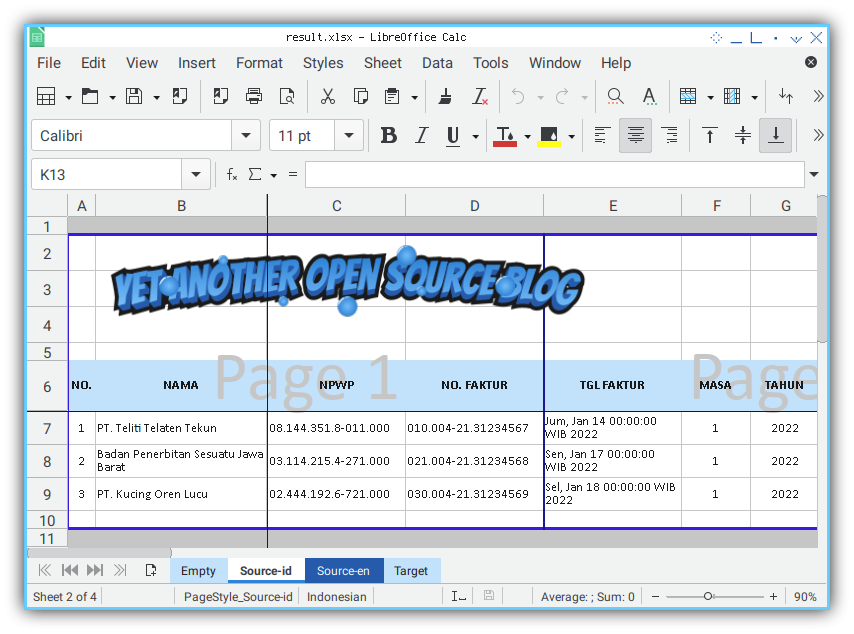
7: Start from Simple
Just make sure you can duplicate the prepared empty worksheet.
Code
Go straight to the code.
For anyone familiar with openpyxl,
there is no need for any basic explanation.
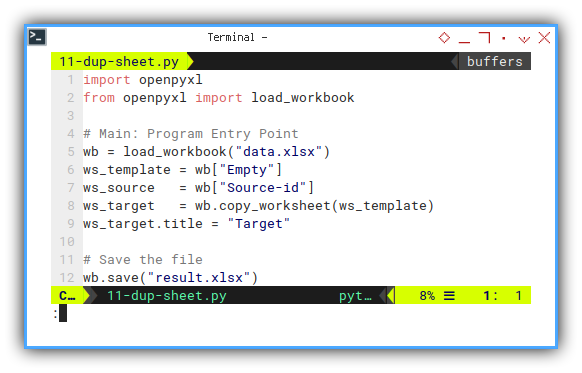
The method responsible is copy_worksheet.
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import load_workbook
# Main: Program Entry Point
wb = load_workbook("data.xlsx")
ws_template = wb["Empty"]
ws_source = wb["Source-id"]
ws_target = wb.copy_worksheet(ws_template)
ws_target.title = "Target"
# Save the file
wb.save("result.xlsx")There is nothing to be shown here.
Just make sure, the openpyxl saved,
into an new file result.xlsx,
with a new sheet named Target.
Result
There is nothing to be shown yet.
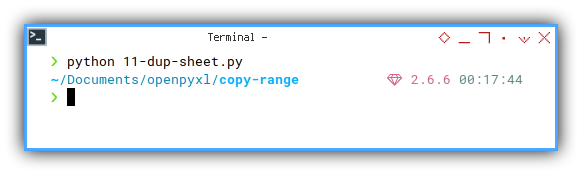
Just open the file and make sure there Target worksheet exist.
8: Fields Mapping
We can begin translating each fields, to predefined location.
Mapping Definition
Again, just put source table, and form view, side by side. And manually defined the field one by one, into a script.
![Worksheet: Source to Target Translation][19-translate]
So you can have this one to one relationship as below:
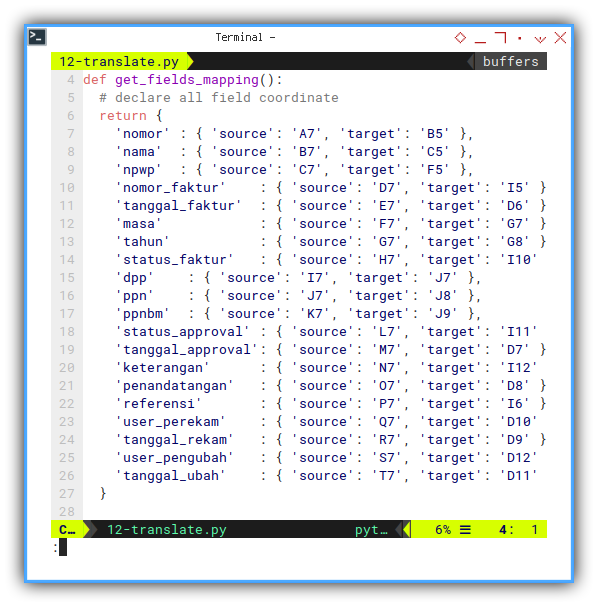
For example in Bahasa Indonesia:
def get_fields_mapping():
# declare all field coordinate
return {
'nomor' : { 'source': 'A7', 'target': 'B5' },
'nama' : { 'source': 'B7', 'target': 'C5' },
'npwp' : { 'source': 'C7', 'target': 'F5' },
'nomor_faktur' : { 'source': 'D7', 'target': 'I5' },
'tanggal_faktur' : { 'source': 'E7', 'target': 'D6' },
'masa' : { 'source': 'F7', 'target': 'G7' },
'tahun' : { 'source': 'G7', 'target': 'G8' },
'status_faktur' : { 'source': 'H7', 'target': 'I10' },
'dpp' : { 'source': 'I7', 'target': 'J7' },
'ppn' : { 'source': 'J7', 'target': 'J8' },
'ppnbm' : { 'source': 'K7', 'target': 'J9' },
'status_approval' : { 'source': 'L7', 'target': 'I11' },
'tanggal_approval': { 'source': 'M7', 'target': 'D7' },
'keterangan' : { 'source': 'N7', 'target': 'I12' },
'penandatangan' : { 'source': 'O7', 'target': 'D8' },
'referensi' : { 'source': 'P7', 'target': 'I6' },
'user_perekam' : { 'source': 'Q7', 'target': 'D10' },
'tanggal_rekam' : { 'source': 'R7', 'target': 'D9' },
'user_pengubah' : { 'source': 'S7', 'target': 'D12' },
'tanggal_ubah' : { 'source': 'T7', 'target': 'D11' },
}You can ignore the name completly. I just put the field name as annotation.
Using Mapping
For first row, it is as simply as copy value from source to target.
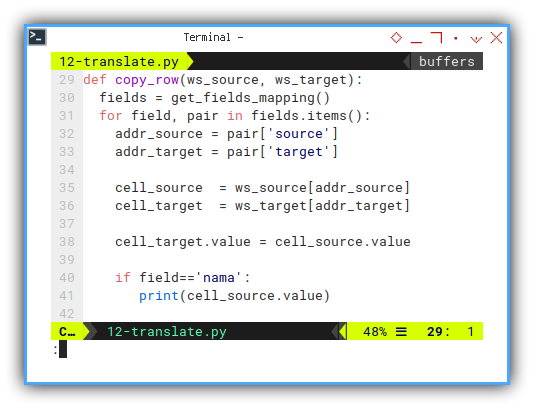
def copy_row(ws_source, ws_target):
fields = get_fields_mapping()
for field, pair in fields.items():
addr_source = pair['source']
addr_target = pair['target']
cell_source = ws_source[addr_source]
cell_target = ws_target[addr_target]
cell_target.value = cell_source.value
if field=='nama':
print(cell_source.value)Execute
You can choose, any language,
en for english, and id for Indonesia.
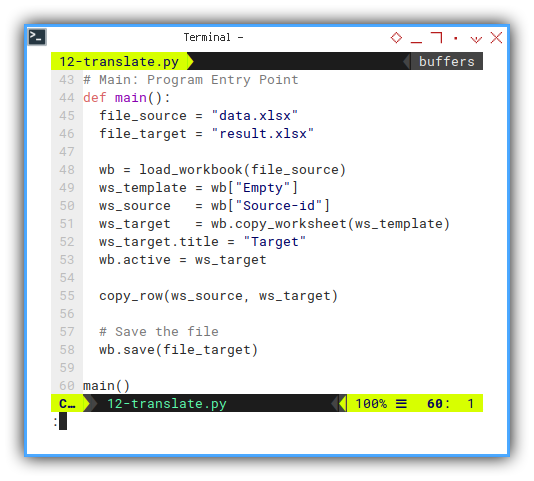
# Main: Program Entry Point
def main():
file_source = "data.xlsx"
file_target = "result.xlsx"
wb = load_workbook(file_source)
ws_template = wb["Empty"]
ws_source = wb["Source-id"]
ws_target = wb.copy_worksheet(ws_template)
ws_target.title = "Target"
wb.active = ws_target
copy_row(ws_source, ws_target)
# Save the file
wb.save(file_target)
main()Result: CLI
Now we also want to dump each process to CLI.
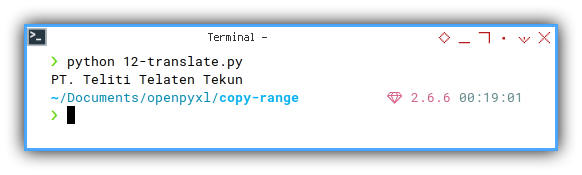
$ python 12-translate.py
PT. Teliti Telaten TekunResult: Sheet
And most importantly the result in sheet. For example in Bahasa Indonesia.
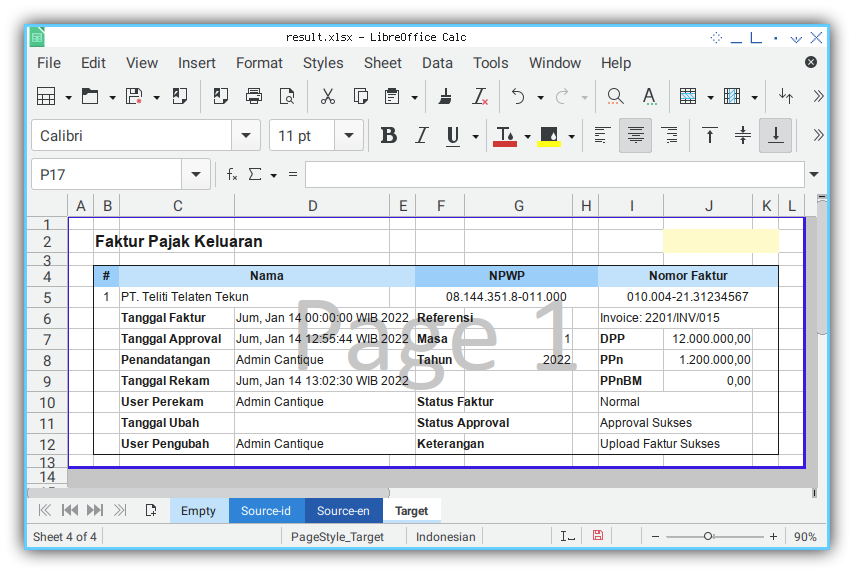
But hey? Only one field??
9: Simple Translate Class
Since we have already know how to work this out. We can start redesign using class.
Skeleton
All definition shown here:
import ...
class TranslateRow:
def __init__(self, ws_source, ws_target):
def get_fields_mapping(self):
def run(self, start, end):
def main():
main()Import
We need a few import statement.
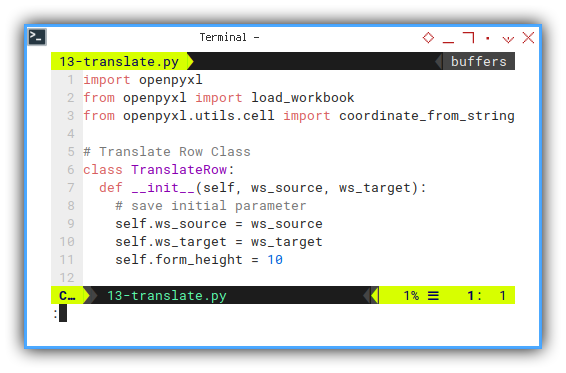
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.utils.cell import coordinate_from_stringClass Initialization
We can start all in initialization.
class TranslateRow:
def __init__(self, ws_source, ws_target):
# save initial parameter
self.ws_source = ws_source
self.ws_target = ws_target
self.form_height = 10Mapping Definition
We can utilize the english version. So you can have this below:
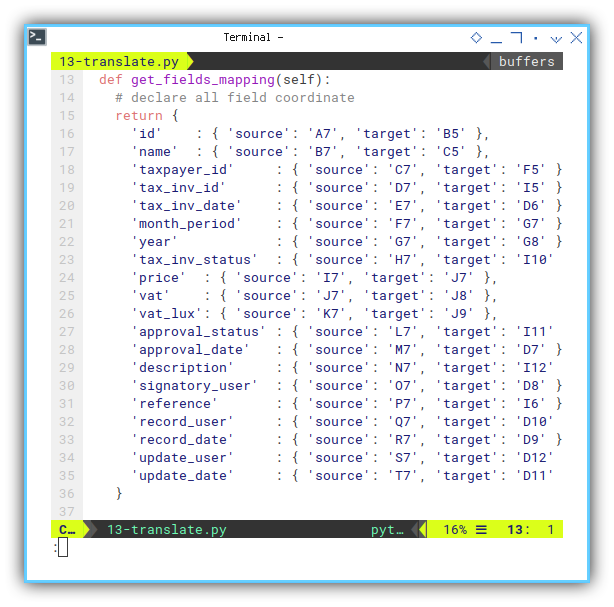
def get_fields_mapping(self):
# declare all field coordinate
return {
'id' : { 'source': 'A7', 'target': 'B5' },
'name' : { 'source': 'B7', 'target': 'C5' },
'taxpayer_id' : { 'source': 'C7', 'target': 'F5' },
'tax_inv_id' : { 'source': 'D7', 'target': 'I5' },
'tax_inv_date' : { 'source': 'E7', 'target': 'D6' },
'month_period' : { 'source': 'F7', 'target': 'G7' },
'year' : { 'source': 'G7', 'target': 'G8' },
'tax_inv_status' : { 'source': 'H7', 'target': 'I10' },
'price' : { 'source': 'I7', 'target': 'J7' },
'vat' : { 'source': 'J7', 'target': 'J8' },
'vat_lux': { 'source': 'K7', 'target': 'J9' },
'approval_status' : { 'source': 'L7', 'target': 'I11' },
'approval_date' : { 'source': 'M7', 'target': 'D7' },
'description' : { 'source': 'N7', 'target': 'I12' },
'signatory_user' : { 'source': 'O7', 'target': 'D8' },
'reference' : { 'source': 'P7', 'target': 'I6' },
'record_user' : { 'source': 'Q7', 'target': 'D10' },
'record_date' : { 'source': 'R7', 'target': 'D9' },
'update_user' : { 'source': 'S7', 'target': 'D12' },
'update_date' : { 'source': 'T7', 'target': 'D11' },
}Reference
Just a reference.
This mapping act as reference.
For example name with source cell address as B7,
will have target cell address as C5.
This work for first row.
How about second row?
The name will have source cell address as B8,
But the target cell address would not be as C6.
With offset 10,
the target cell address would not be as C16.
This applied with third row.
The name will have source cell address as B9,
And the target cell address would be as C17.
Run: Execute
It is getting longer. I will explain later.
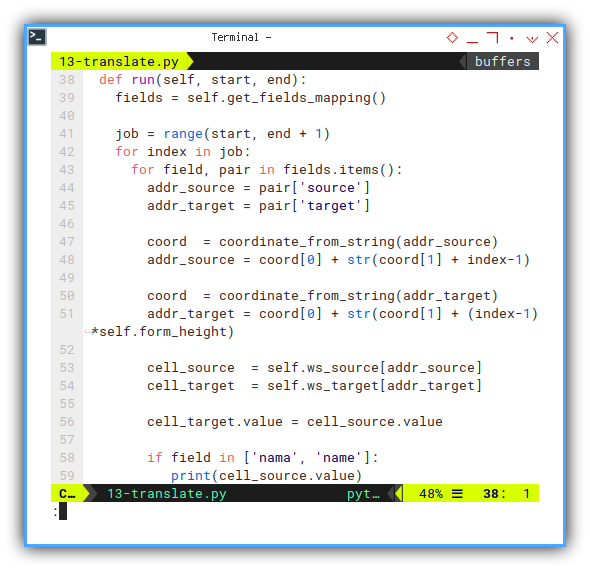
def run(self, start, end):
fields = self.get_fields_mapping()
job = range(start, end + 1)
for index in job:
for field, pair in fields.items():
addr_source = pair['source']
addr_target = pair['target']
coord = coordinate_from_string(addr_source)
addr_source = coord[0] + str(coord[1] + index-1)
coord = coordinate_from_string(addr_target)
addr_target = coord[0] + str(coord[1] + (index-1)*self.form_height)
cell_source = self.ws_source[addr_source]
cell_target = self.ws_target[addr_target]
cell_target.value = cell_source.value
if field in ['nama', 'name']:
print(cell_source.value)Main
It is getting longer. I will explain later.
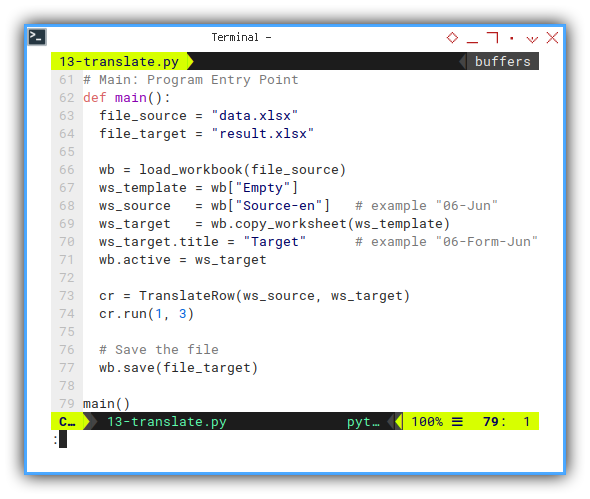
def main():
file_source = "data.xlsx"
file_target = "result.xlsx"
wb = load_workbook(file_source)
ws_template = wb["Empty"]
ws_source = wb["Source-en"] # example "06-Jun"
ws_target = wb.copy_worksheet(ws_template)
ws_target.title = "Target" # example "06-Form-Jun"
wb.active = ws_target
cr = TranslateRow(ws_source, ws_target)
cr.run(1, 3)
# Save the file
wb.save(file_target)
main()Result: CLI
Now we can see each process to CLI.

$ python 13-translate.py
Earth Wind And Flour, Ltd
The Office of Space Racoon Protection
Four Purr Furr, IncResult: Sheet
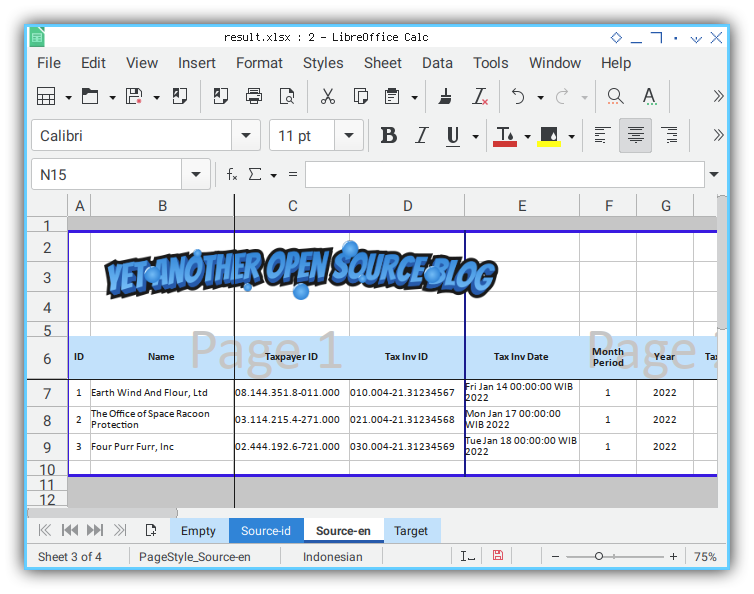
The result are good. But the looks is terrible, because we have’nt copy the template yet. as shown in figure below:
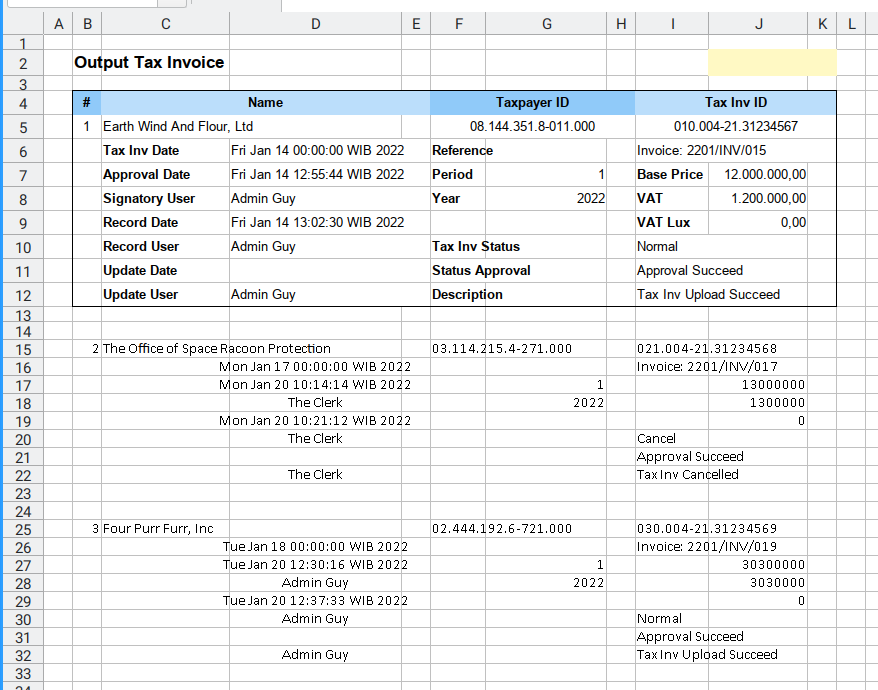
The figure is based on the english source.
Using the Script.
For the real case, this is other example, a year report, contain each months.
To reduce complexity, The target file is also “data.xslx”
def main():
file_source = "data.xlsx"
file_target = "result.xlsx"
...Imagine that the source is already separated sheet by month:
01-Jan, three rows02-Feb, five rows03-Mar, seven rows
Now I can manually edit the entry, for example this January:
def main():
...
ws_source = wb["01-Jan"]
ws_target = wb.copy_worksheet(ws_template)
ws_target.title = "01-F-Jan"
wb.active = ws_target
cr = TranslateRow(ws_source, ws_target)
cr.run(1, 3)
...Execute, the manually edit:
def main():
...
ws_source = wb["02-Feb"]
ws_target = wb.copy_worksheet(ws_template)
ws_target.title = "02-F-Feb"
wb.active = ws_target
cr = TranslateRow(ws_source, ws_target)
cr.run(1, 5)
...And so on.
You might want to automate the loop also, for recurring job.
So you do not need to type 01-Jan, 02-Feb, and so on.
10: Using Both Class
This is our final form in this article.
But I bet, you want to enhance the script yourself, into more useful classes. Or merge them into just one classes. Depend on your case.
Skeleton
All definition shown here:
import ...
class CopyRange:
def __init__(self, sheet, coord_copied):
def copy_cells(self):
def set_row_height(self):
def set_merged_range(self):
def run(self, offset_down):
class TranslateRow:
def __init__(self, ws_source, ws_target):
def get_fields_mapping(self):
def run(self, start, end):
def main():
main()The Copy Range Class are called within the Translate Row class.
The Copy Range Class
Nothing change.
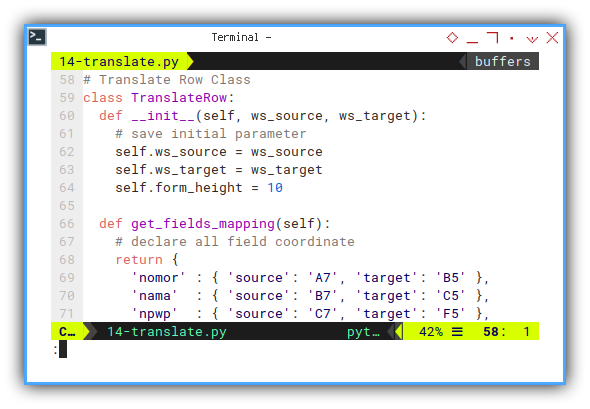
The Translate Row Class
Almost no change, except adjustment in run method.
Execute: Run
Just a few additional adjustment. In the heart of this class.
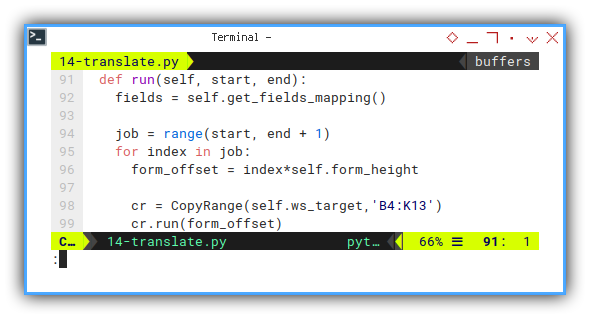
def run(self, start, end):
fields = self.get_fields_mapping()
job = range(start, end + 1)
for index in job:
cr = CopyRange(self.ws_target,'B4:K13')
cr.run(form_offset)But I think it’s better to get,
only one instance of CopyRange at the top.
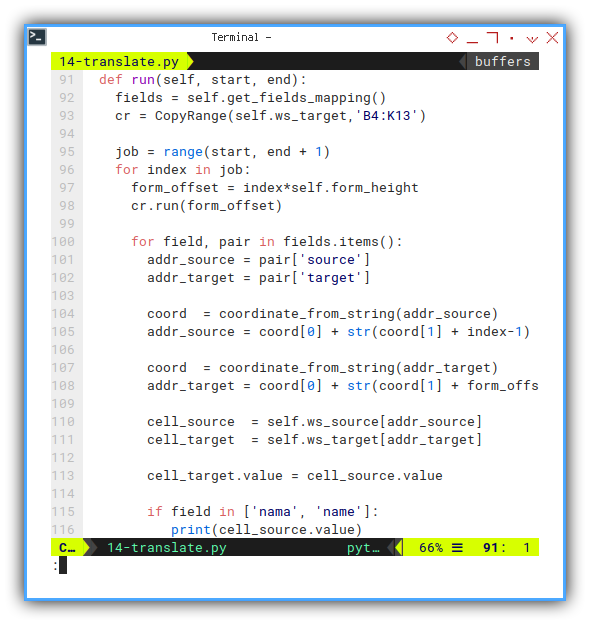
def run(self, start, end):
fields = self.get_fields_mapping()
cr = CopyRange(self.ws_target,'B4:K13')
job = range(start, end + 1)
for index in job:
form_offset = index*self.form_height
cr.run(form_offset)
for field, pair in fields.items():
addr_source = pair['source']
addr_target = pair['target']
coord = coordinate_from_string(addr_source)
addr_source = coord[0] + str(coord[1] + index-1)
coord = coordinate_from_string(addr_target)
addr_target = coord[0] + str(coord[1] + form_offset)
cell_source = self.ws_source[addr_source]
cell_target = self.ws_target[addr_target]
cell_target.value = cell_source.value
if field in ['nama', 'name']:
print(cell_source.value)Result: CLI
again, check each process to CLI.

$ python 14-translate.py
Earth Wind And Flour, Ltd
The Office of Space Racoon Protection
Four Purr Furr, IncResult: Sheet
The result are good. And the looks is also good now.
Beyond The Script
This script is intended to be modified to suit your needs.
For finishing you can manually delete rows, containing empty form on the top most. You can also develop your own script to suit yor need, for example, you can divide the data for the whole year, and then put them in different sheet for each related month.
But that is beyond my example. The possibility is to broad, depend on the nature of your data.
Happy Coding!
Export
With LibreOffice,
We can export the result into png ot pdf.
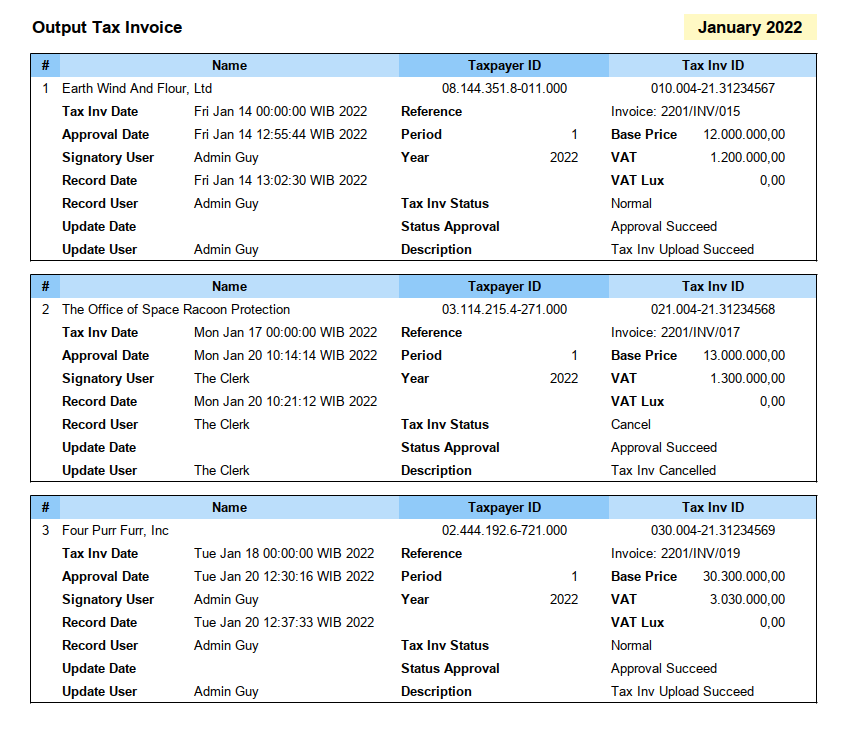
Although administrating is fun! I think we are done here.
Conclusion
We are done. That is all. Thank you for reading.
Maybe another article, another time. What do you think?