Preface
Goal: Copy A Range of Cell Along with All Properties.
This article is the first part of two articles.
Proper document handling is required, when your quiet messy company, suddenly audited by public accountant.
Although the view below using LibreOffice, the example is excel files. You can open the spreadsheet using Excel.
1: The Challenge
Tidying? Don’t you have better thing to do?
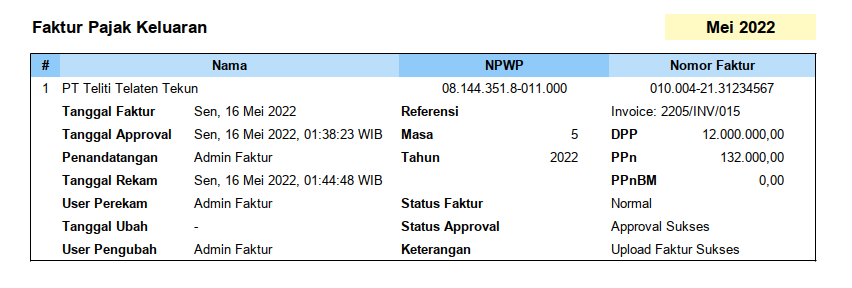
Have you ever on your job met a spreadsheet with a so many table header, sooo long, that you can’t even print without additional paper?
For example this sheet below:
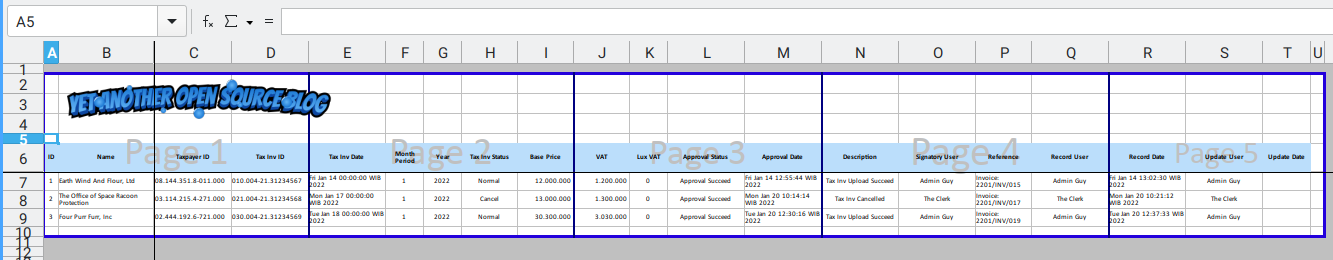
And when you print the table:
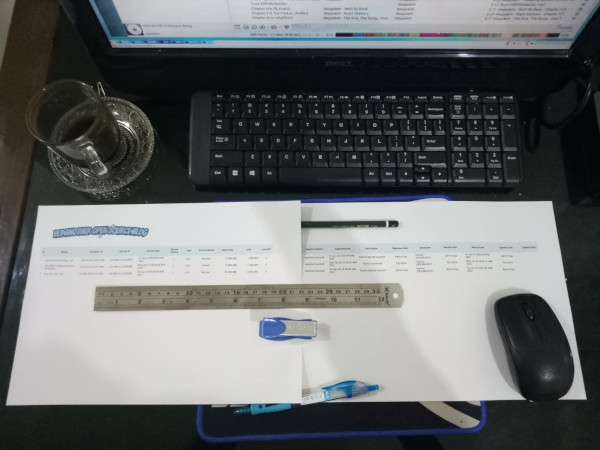

Actually you can translate the table looks, into form view as below, with just simple translation script.
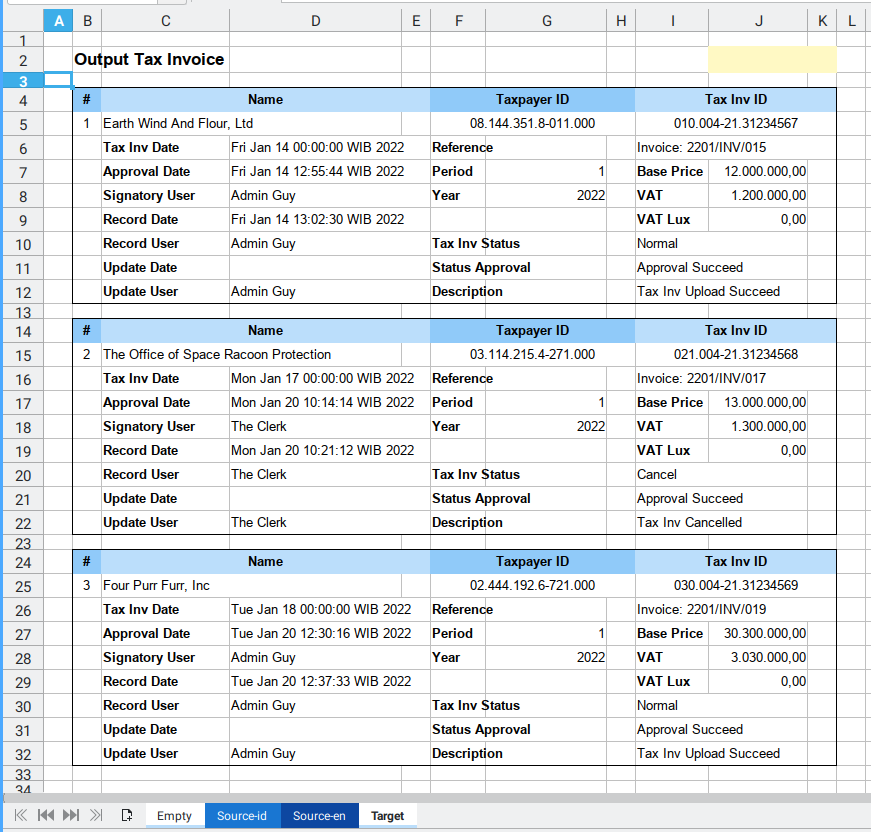
The real life printed result can be seen as below:
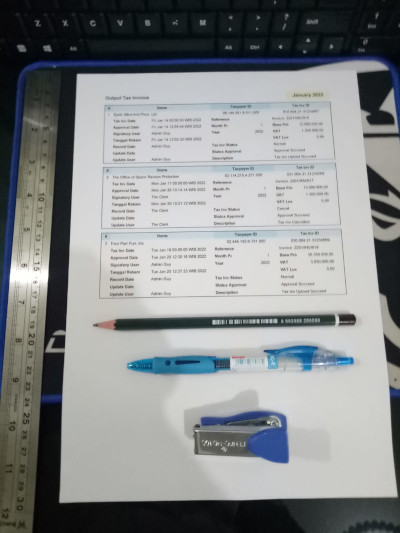
It is easy, when all you have is just those two row of data as above. But how about thousands of data? You can create yourself a script. Execute, and voila, those thousand rows is already exported, into the form.
cuman orang gabut yang sempet ngerapi-rapi-in
Designing Template
Our challenge is field translation. Before we ever need to translate, we need to create a template.
All I do is just put source table, and form view, side by side. And manually moved the field one by one.
This task is not as easy as I was thinking. I need to create a few design, and designing form takes cycle.
- The first one are scrapped directly.
- The second one evolved into the third
- I choose the third one
- In implementation, I suddenly make the fourth based on the third one.
- I finally make final changes, for different language. The fifth form design.
Fields in Detail
Dual Language
Since I my original tutorial based on goverment tax field in Indonesia, I have to create the english version, so you understand, what the meaning of each example.
Consider have a look at all fields in detail. I provide two language for each: English and Indonesia.
- Fields: Screenshot One
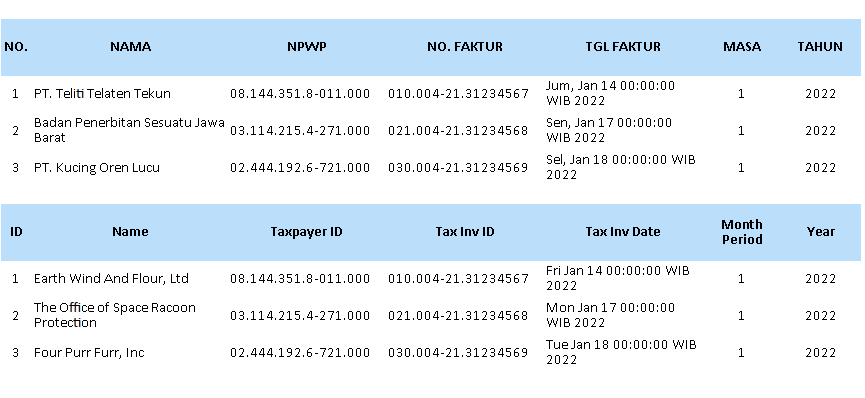
- Fields: Screenshot Two
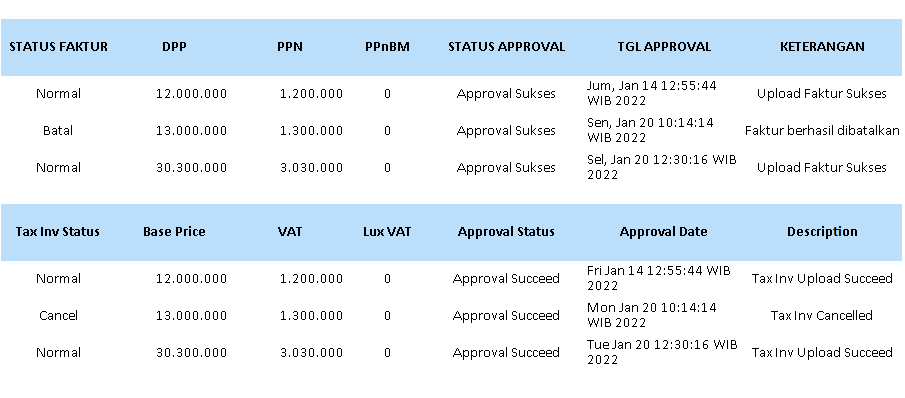
- Fields: Screenshot Three
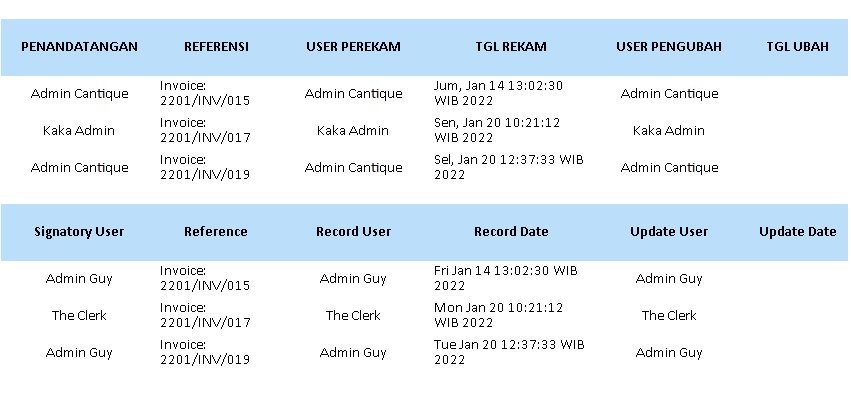
Excuse my english, also apologize for my lack knowledge of tax terminology.
Copying Issue
Have you ever have a difficulties to copy cells range programatically?
Copying cells using openpyxl require copying of these three attributes:
- Basic Attribute: Value, Style, and Number Format
- Row Height
- Merge Cells
2: Using OpenPyXL
Example Data
I have provided example sheets, with complete form, along with each properties. Such as different number format and so on.
You can download the source here
Along with the result also
Each sheet, I provide two languages. You should choose only one over another.
- Source Sheet: English
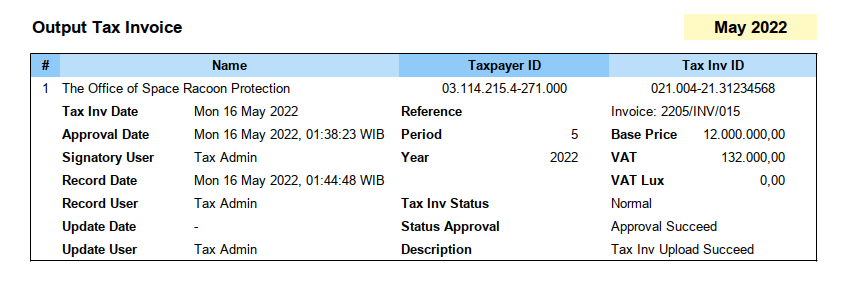
- Source Sheet: Indonesia
Code
Testing
I always have this fear when I start something new, so I push myself to start code as small as possible, then suddenly my fear vanished.
Go straight to the code. Start from simple. Just open file and save.
There is only consist one short file required.
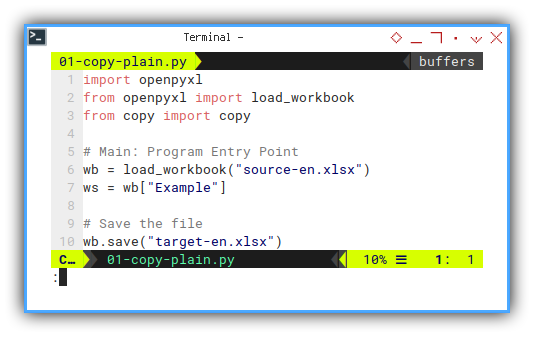
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from copy import copy
# Main: Program Entry Point
wb = load_workbook("source-en.xlsx")
ws = wb["Example"]
# Save the file
wb.save("target-en.xlsx")There is nothing to be shown here.
Just make sure, the openpyxl saved,
into an new file target-en.xlsx.
3: Procedural Code
I have made a procedural code, as my starting point. It works but it is considered barbaric.
But we won’t use this, because I want to use class based.
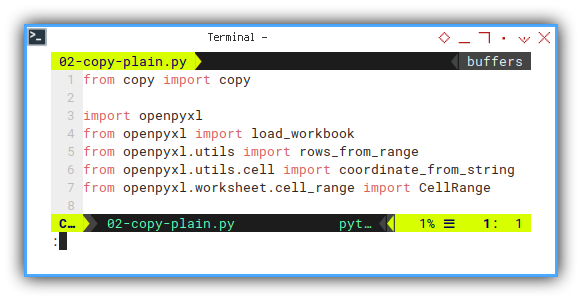
from copy import copy
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.utils import rows_from_range
from openpyxl.utils.cell import coordinate_from_string
from openpyxl.worksheet.cell_range import CellRange
def copy_range(coord_copied, sheet, offset_down):
# row height related
wsrd = sheet.row_dimensions
for row in rows_from_range(coord_copied):
# value, style and number format
for cell in row:
coord = coordinate_from_string(cell)
offset = coord[0] + str(coord[1] + offset_down)
source = sheet[cell]
target = sheet[offset]
target.value = source.value
target.number_format = source.number_format
if source.has_style:
target._style = copy(source._style)
# row height
first = row[0]
coord = coordinate_from_string(first)
source = wsrd[coord[1]]
target = wsrd[coord[1] + offset_down]
target.height = source.height
# merged range
range_copied = CellRange(coord_copied)
for merged_cell in sheet.merged_cells:
coord_source = merged_cell.coord
if coord_source in range_copied:
cell_range = CellRange(coord_source)
cell_range.shift(row_shift = offset_down)
coord_target = cell_range.coord
sheet.merge_cells(coord_target)
# Main: Program Entry Point
wb = load_workbook("source-en.xlsx")
ws = wb["Example"]
copy_range ('B4:K13', ws, 10)
# Save the file
wb.save("target-en.xlsx")Just one function, no class. Bad practice. But good for starting point.
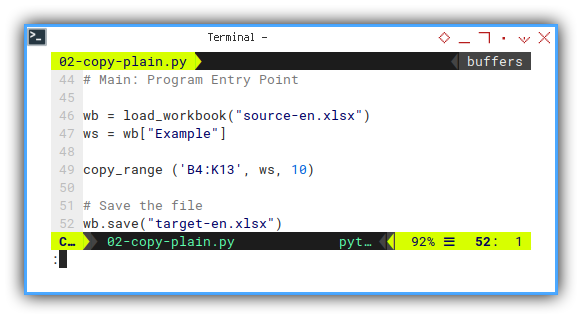
Now let’s start all over again. Refactoring.
4: Simple Copy Class
A class, just copy the range.
Skeleton
All definition shown here:
import ...
class CopyRange:
def __init__(self, sheet, coord_copied):
def copy_cells(self, offset_down):
def main():
main()So simple, that this class only have one method, the copy_cells.
Import
We need a few import statement.
import re
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import (Color,
PatternFill, Font, Border, Alignment)
from openpyxl.utils.cell import get_column_letterClass Initialization
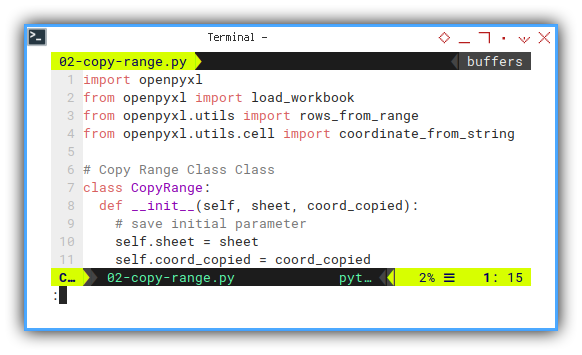
We can start all in initialization.
class CopyRange:
def __init__(self, sheet, coord_copied):
# save initial parameter
self.sheet = sheet
self.coord_copied = coord_copiedCopy Cells Method
The real horse work here.
It is self explanatory. Get the coordinate, then copy all properties.
- value,
- style and,
- number format
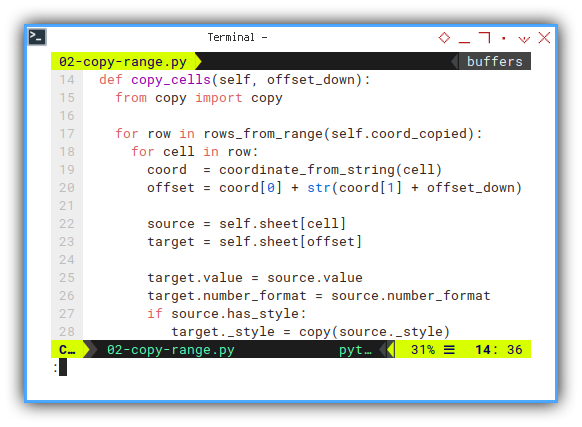
def copy_cells(self, offset_down):
from copy import copy
for row in rows_from_range(self.coord_copied):
for cell in row:
coord = coordinate_from_string(cell)
offset = coord[0] + str(coord[1] + offset_down)
source = self.sheet[cell]
target = self.sheet[offset]
target.value = source.value
target.number_format = source.number_format
if source.has_style:
target._style = copy(source._style)Form Offset
What is it, this strange offset_down anyway?
This is the height of the form.
For example this form,
this has 10 stacked rows including header.
If the reference start from B4 cell address,
then the first copy should be B14,
the second should be B24, and so on.
We will automate by making loop later, but for starter let’s do this manually, by calling the method.
cr.copy_cells(10)
cr.copy_cells(20)And so on.
Execute
Program Entry Point
Yes, the I usually named the function as main.
Although you can name it anything you want.
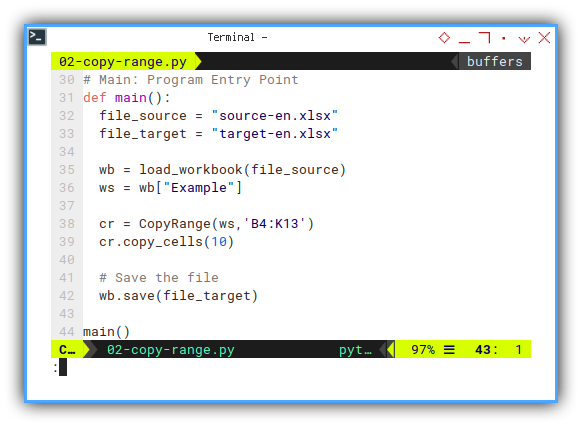
def main():
file_source = "source-en.xlsx"
file_target = "target-en.xlsx"
wb = load_workbook(file_source)
ws = wb["Example"]
cr = CopyRange(ws,'B4:K13')
cr.copy_cells(10)
# Save the file
wb.save(file_target)
main()Notice that I set offset_down parameter to ten.
This is the height of the form,
as we have already explained above.
Result
The result are terrible, as shown in figure below:
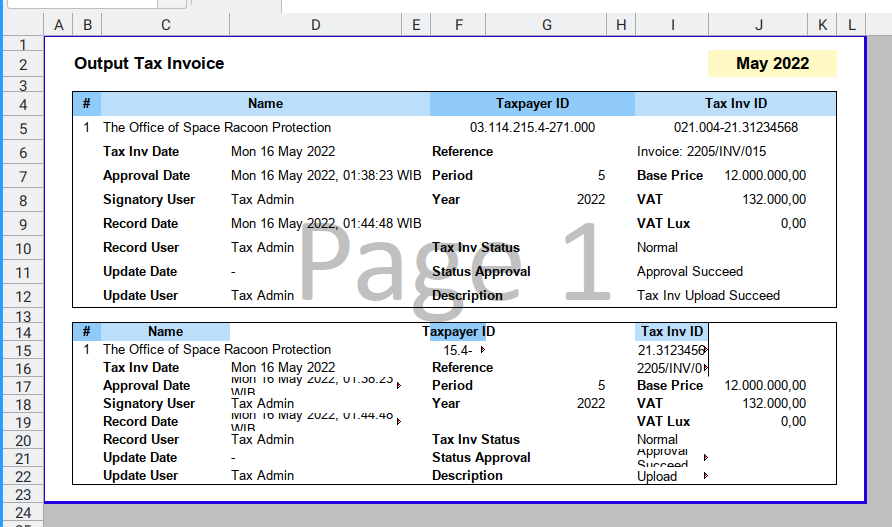
The figure is based on the english source.
What’s Wrong?
Missing Something?
We need to also set merge cell, and also copy the row height properties.
5: Complete Copy Class
A class, with complete copying, including height and merge.
Skeleton
All definition shown here:
import ...
class CopyRange:
def __init__(self, sheet, coord_copied):
def copy_cells(self):
def set_row_height(self):
def set_merged_range(self):
def run(self, offset_down):
def main():
main()It is self explanatory.
Import
Import statement as usual:
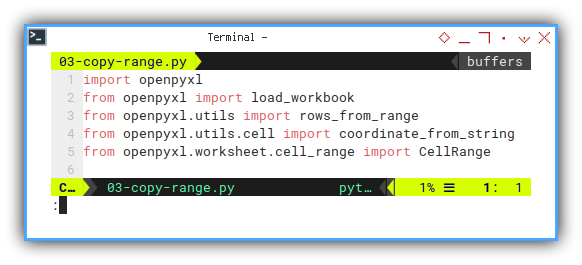
import openpyxl
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.utils import rows_from_range
from openpyxl.utils.cell import coordinate_from_string
from openpyxl.worksheet.cell_range import CellRangeInit
Import statement as usual:
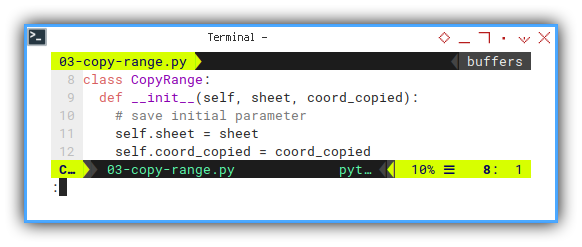
class CopyRange:
def __init__(self, sheet, coord_copied):
# save initial parameter
self.sheet = sheet
self.coord_copied = coord_copiedMain
Consider jump to the end before dive to detail.
The main function can be defined as this below:
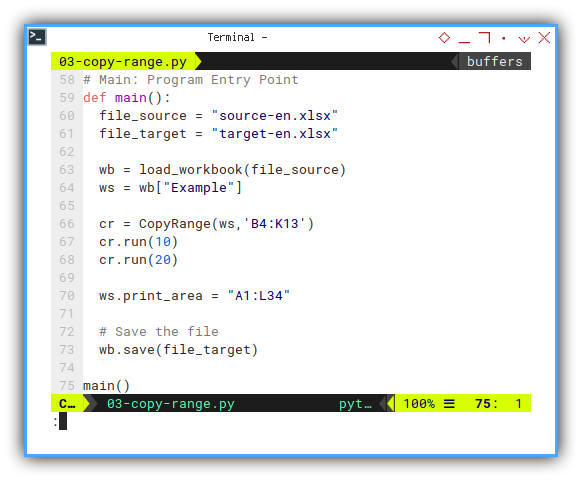
def main():
file_source = "source-en.xlsx"
file_target = "target-en.xlsx"
wb = load_workbook(file_source)
ws = wb["Example"]
cr = CopyRange(ws,'B4:K13')
cr.run(10)
cr.run(20)
ws.print_area = "A1:L34"
# Save the file
wb.save(file_target)
main()Run: Execute
The run method is just gathering of copying function.
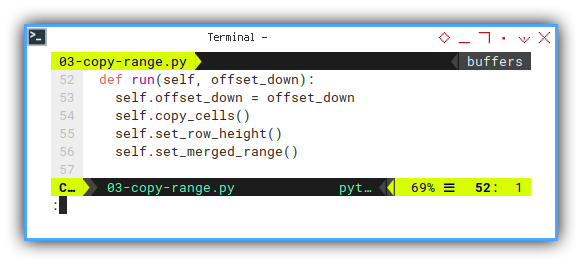
def run(self, offset_down):
self.offset_down = offset_down
self.copy_cells()
self.set_row_height()
self.set_merged_range()Now we should be ready to see each of these three functions.
Copy Cells
This is almost the same as our previous example.
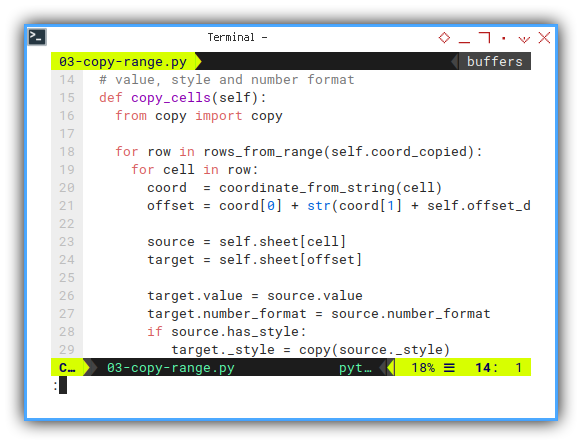
# value, style and number format
def copy_cells(self):
from copy import copy
for row in rows_from_range(self.coord_copied):
for cell in row:
coord = coordinate_from_string(cell)
offset = coord[0] + str(coord[1] + self.offset_down)
source = self.sheet[cell]
target = self.sheet[offset]
target.value = source.value
target.number_format = source.number_format
if source.has_style:
target._style = copy(source._style)The same as previous code.
Not really verbatim copy.
Because I move the offset_down,
into class property, instead of parameter argument.
Setting Row height
Instead of cells, we work with rows.
To be exact, the responsible object is row_dimensions.
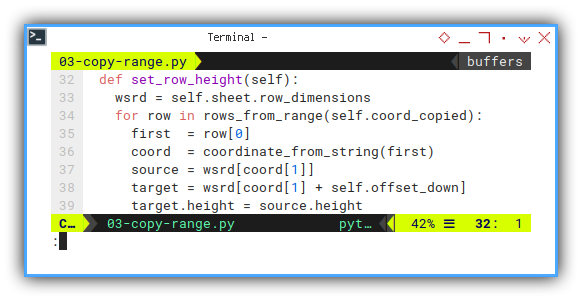
# row height related
def set_row_height(self):
wsrd = self.sheet.row_dimensions
for row in rows_from_range(self.coord_copied):
first = row[0]
coord = coordinate_from_string(first)
source = wsrd[coord[1]]
target = wsrd[coord[1] + self.offset_down]
target.height = source.heightAnd yeah, we also require the offset_down reference.
Setting Merged Range
This is the code I learned from stackoveflow somewhere a long time ago. I’m not sure how many changes I have alter, from the original code.
The property responsible for this is merged_cells.
And the method is merge_cells.
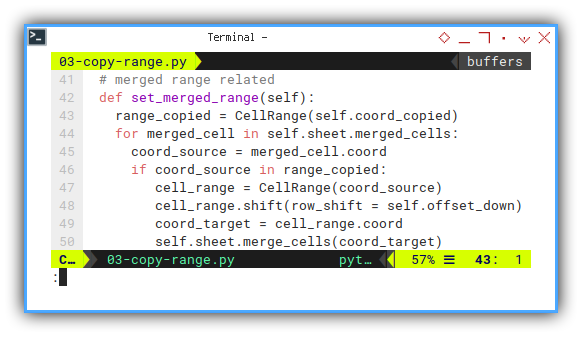
# merged range related
def set_merged_range(self):
range_copied = CellRange(self.coord_copied)
for merged_cell in self.sheet.merged_cells:
coord_source = merged_cell.coord
if coord_source in range_copied:
cell_range = CellRange(coord_source)
cell_range.shift(row_shift = self.offset_down)
coord_target = cell_range.coord
self.sheet.merge_cells(coord_target)First to do is to iterate all merged cells. If it is within the copied range, then process.
For each merged cell processed,
we have to switch form cell coordinate to range.
Shift the row range by the offset_down number.
And finally merge the cell in new form.
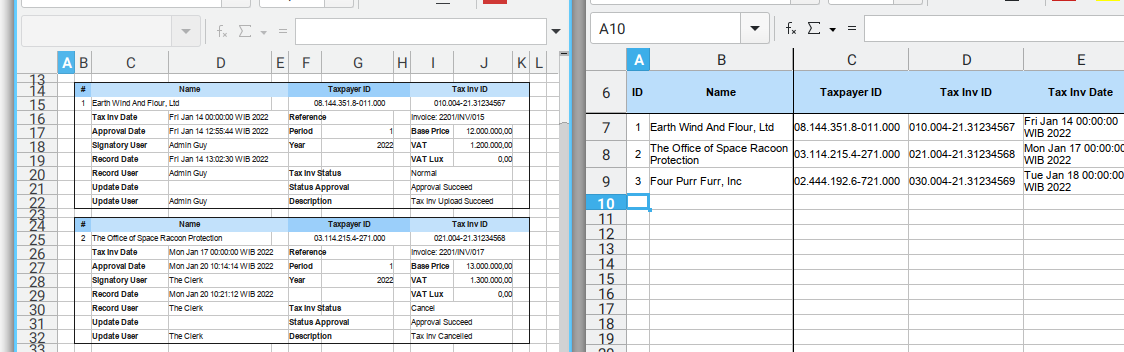
Result
The result are verbatim copy, as shown in figure below:
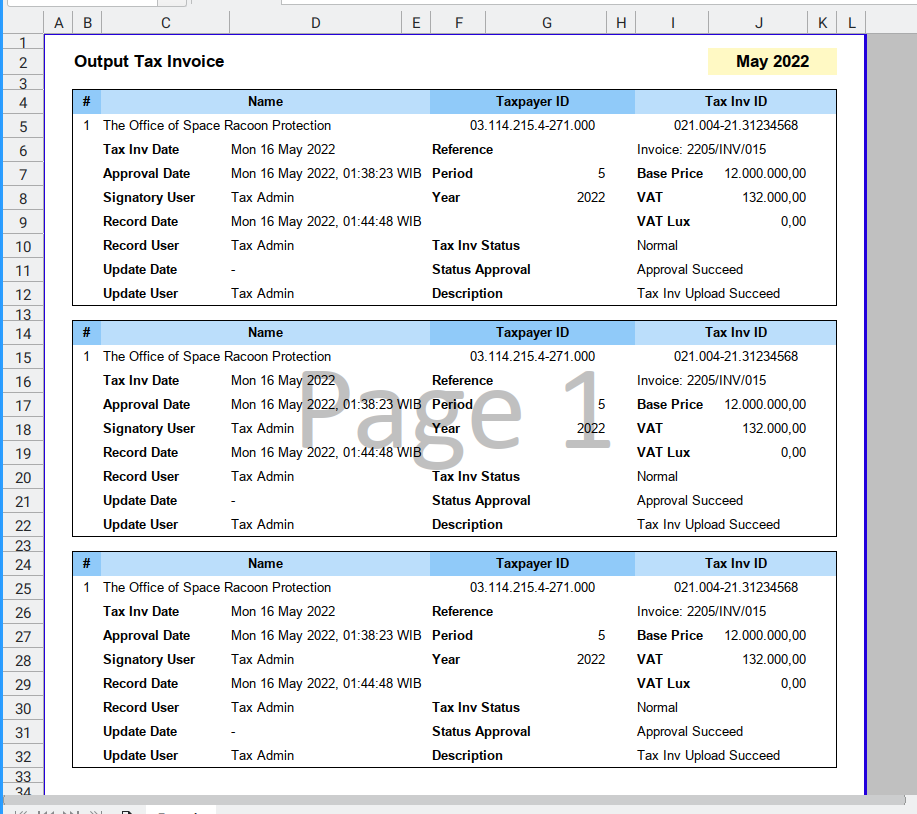
The first copy is using offset_down = 10,
and the next copy is using offset_down = 20.
While the original source remain intact.
cr = CopyRange(ws,'B4:K13')
cr.run(10)
cr.run(20)We are done copying cell here.
What is Next 🤔?
After copying range of cells, now is a good time to continue to fields translation.
Consider continue reading [ Python - Excel - Translate Field ].